Antikythera Mechanism: The Ancient Greek Computer
Unraveling the Mystery of the Antikythera Mechanism
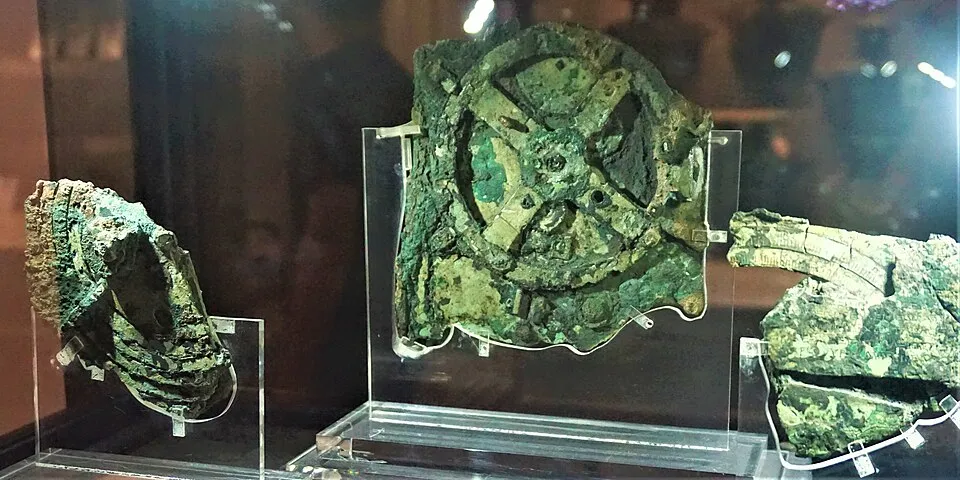

Fragment of the Antikythera Mechanism at the National Archaeological Museum, Athens. Year: early 20th century discovery. By Joyofmuseums.
License: CC BY-SA 4.0. link
The Antikythera Mechanism is one of the most fascinating discoveries of archaeology, often called the world’s first computer. Found in 1901 in a shipwreck off the Greek island of Antikythera, this mysterious device was unlike anything else from antiquity. It consisted of intricate bronze gears housed in a wooden box, capable of calculating celestial events, predicting eclipses, and tracking the cycles of the ancient Greek calendar.
At first glance, it looked like a corroded lump of bronze. Yet over time, researchers realized it represented a technological leap far ahead of its time. To this day, the Antikythera Mechanism sparks debates, inspiring both scientists and dreamers about the ingenuity of ancient civilizations.
How the Antikythera Mechanism Worked
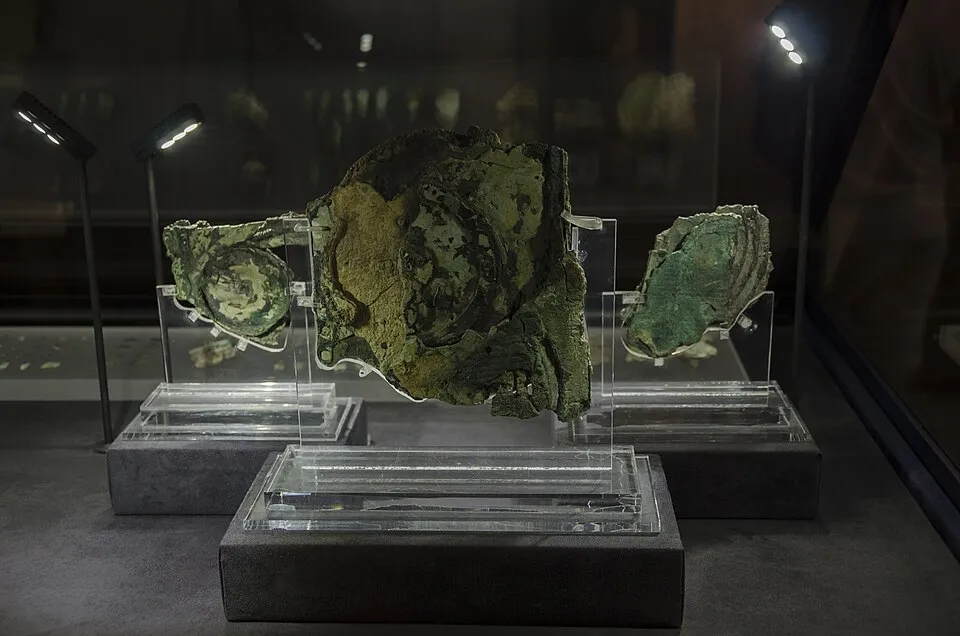

Detailed view of Antikythera Mechanism pieces, National Archaeological Museum 2017. Year: 2017. By Peulle. License: CC BY-SA 4.0. link
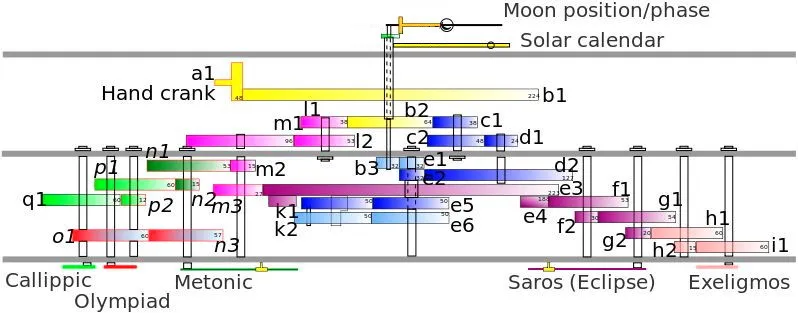
The Antikythera Mechanism contained at least 30 interlocking bronze gears, some as fine as modern clockwork. By turning a hand-crank, ancient Greeks could simulate the movement of the Sun, the Moon, and possibly even the five known planets. Its front dial showed the zodiac and solar calendar, while the back displayed eclipse predictions and cycles like the Saros period.
What amazes scientists is not just the function but the craftsmanship. The gear teeth were cut with astonishing precision. The mechanism could track the irregular orbit of the Moon, a feat thought impossible for ancient engineers. This combination of astronomy, mathematics, and mechanics makes it the most advanced surviving artifact of Hellenistic technology.
Rediscovery and Modern Investigations
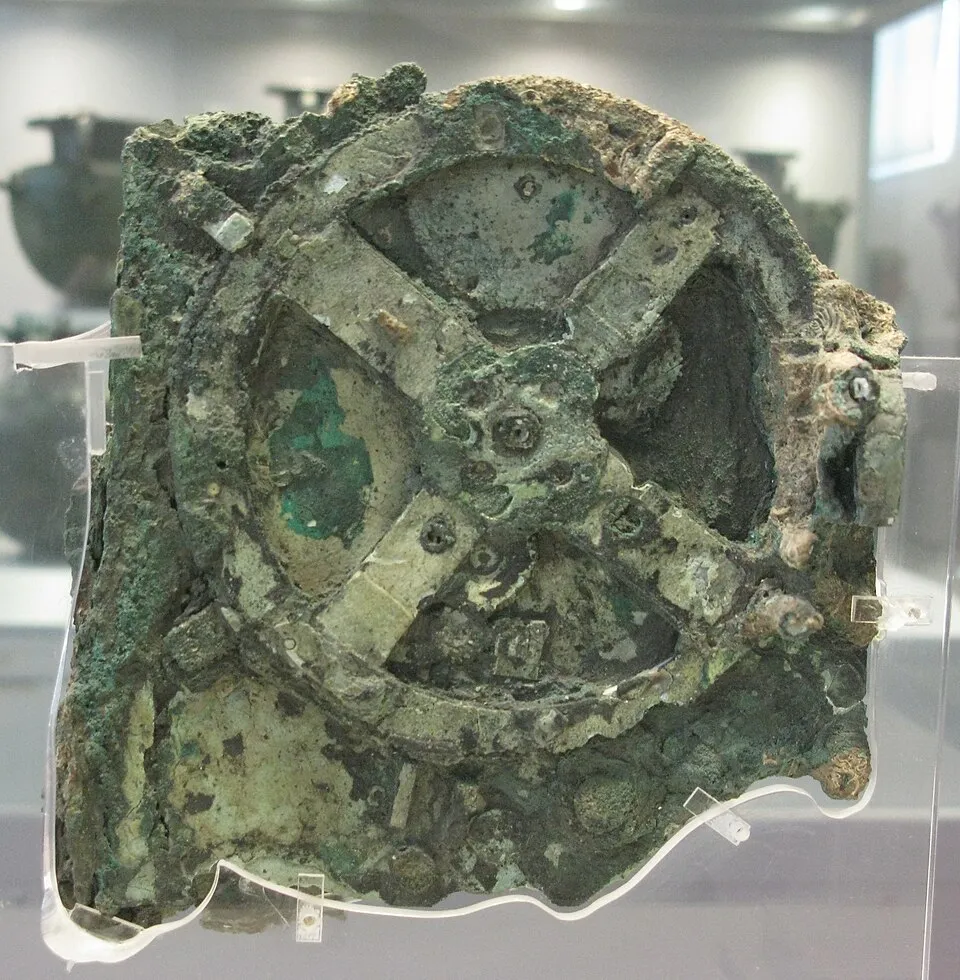

High-resolution photograph of corroded gear wheels from the Antikythera Mechanism. Year: 20th century find. By Tilemahos Efthimiadis. License: CC BY 2.0. link
When divers first pulled the mechanism from the seabed, its significance was overlooked. It wasn’t until 1959 that British science historian Derek J. de Solla Price suggested it was an astronomical computer. Later, with advances in imaging technology such as 3D X-ray scans, scientists uncovered inscriptions on the plates, explaining its purpose.
The discovery changed our perception of ancient science. Until then, historians assumed mechanical devices of such complexity appeared in the Middle Ages. Instead, the Antikythera Mechanism proved that Greek engineers two millennia ago had already mastered advanced gear systems.
Reconstructions and Modern Models
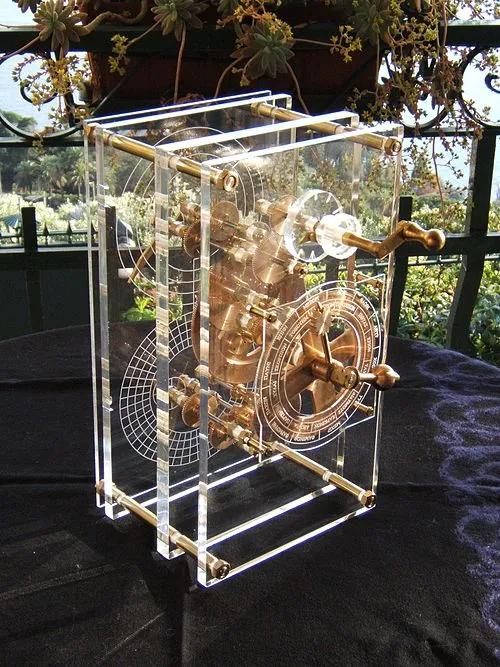

A reconstruction showing the front panel of the Antikythera Mechanism. Year: 2007. By Mogi Vicentini. License: CC BY-SA 3.0. link
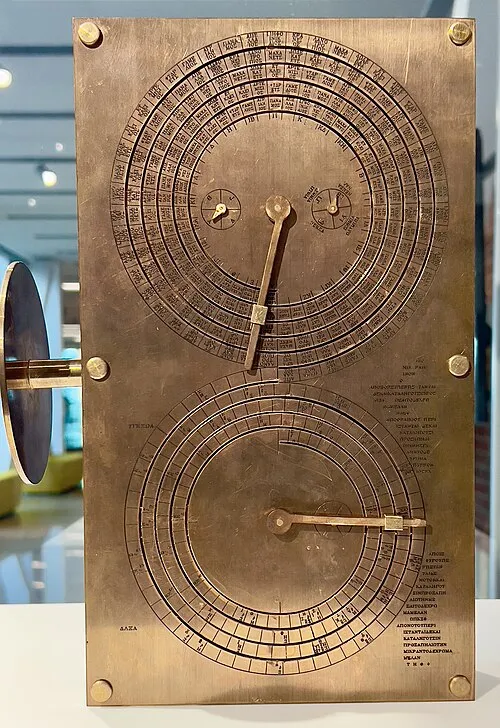
Over the years, researchers have attempted to reconstruct how the device might have looked in its prime. Using ancient descriptions and modern calculations, engineers built working replicas that demonstrate how Greeks could predict eclipses and planetary alignments. These reconstructions show that the mechanism functioned much like a mechanical analog computer — a tool not only of science but of wonder.
Today, visitors can see these reconstructions in museums around the world. They serve as a reminder that knowledge once lost can be rediscovered, and that ancient technology often hides surprises waiting beneath the sea.
Exhibitions and Public Fascination
Museum display dedicated to the Antikythera Mechanism, showing fragments and replicas. Year: 21st century exhibition. By Holdi Sig. License: CC BY-SA 4.0. link
The Antikythera Mechanism is more than an artifact; it has become a cultural icon. Documentaries, books, and even films have been inspired by its mystery. Museums showcase not only the fragments but also digital animations that allow the public to see how it worked.
For many, the Antikythera Mechanism symbolizes the lost knowledge of ancient civilizations. It suggests that humanity once achieved technological heights that were later forgotten, only to be reinvented centuries later. This idea resonates strongly with those fascinated by history, technology, and the resilience of human curiosity.
The Antikythera Mechanism Today

Modern exhibition at WA Museum Boola Bardip showing Antikythera reconstructions. Year: 2023. By Kgbo. License: CC BY-SA 4.0. link

Visitors exploring an interactive reconstruction of the Antikythera Mechanism at WA Museum. Year: 2023. By Kgbo. License: CC BY-SA 4.0. link
Modern exhibitions continue to explore the story of this ancient computer. In 2023, new reconstructions were presented at international museums, blending science with interactive displays. These exhibits allow visitors to turn gears and visualize the cosmos as ancient Greeks once did.
This continuous research not only deepens our understanding of Greek technology but also reminds us how much of history is still hidden. Every new fragment or inscription pushes the boundaries of what we thought possible in antiquity.


